numpy用法
import numpy as ap
numpy主要用来创建vectors和matrics,solve linear operations and generate random entries.
创建数组
- 列表[]构建数组
>>> a = np.array([1,2,3,4])
>>> a.size
4 # 4个元素
>>> a.shape
(4,) # 4行1列
>>> print(a)
[1 2 3 4]
| 数组a |
|---|
| 1 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
| 4 |
- 行列向量转换
>>> a.shape=(1,4)
>>> print(a)
[[1 2 3 4]]
| c1 | c2 | c3 | c4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
>>> a.reshape(2,2)
array([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
| c1 | c2 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2 |
| 3 | 4 |
- 取元素

>>> b = a.reshape(2,2)
>>> print(b)
[[1 2]
[3 4]]
>>> b[0,:] # 取第1行
array([1, 2])
>>> b[:,0] # 取第1列
array([1, 3])
>>> b[0,1] # 取第1行第2列
2
>>> b[1,1] # 取第2行第2列
4
- 改元素
>>> b[0,1] = 9.2 # 改第1行第2列为浮点数9.2
>>> print(b)
[[1 9]
[3 4]]
b矩阵元素统一成浮点型
>>> c = np.array(b,dtype=float)
>>> print(c)
[[1. 9.]
[3. 4.]]
修改c[0,1] = 9.2
>>> c[0,1] = 9.2
>>> print(c)
[[1. 9.2]
[3. 4. ]]
独立copy
>>> d = c.copy()
>>> print(d)
[[1. 9.2]
[3. 4. ]]
>>> d[0,1] = 10.2
>>> print(d)
[[ 1. 10.2]
[ 3. 4. ]]
>>> print(c)
[[1. 9.2]
[3. 4. ]]
- arange
>>> a = np.arange(1,10,2) # 从1开始后续元素加2,不超过10
>>> print(a)
[1 3 5 7 9]
>>> b = np.arange(10,1,-2) # 从10开始后续减2,不超过1
>>> print(b)
[10 8 6 4 2]
>>> d = np.arange(10) # 生成10个元素
>>> print(d)
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
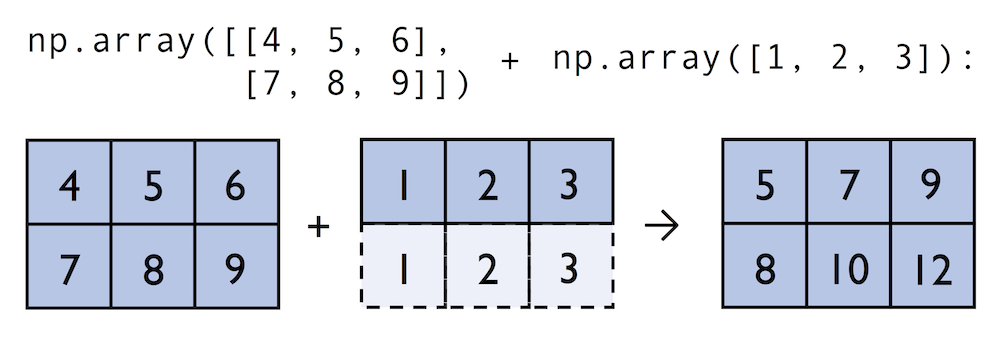
broadcasting
广播(Broadcast)是 numpy 对不同形状(shape)的数组进行数值计算的方式,当运算中的 2 个数组的形状不同时,numpy 将自动触发广播机制;即:可扩充较小数组中的元素来适配较大数组的形状,这种机制叫作广播(broadcasting)
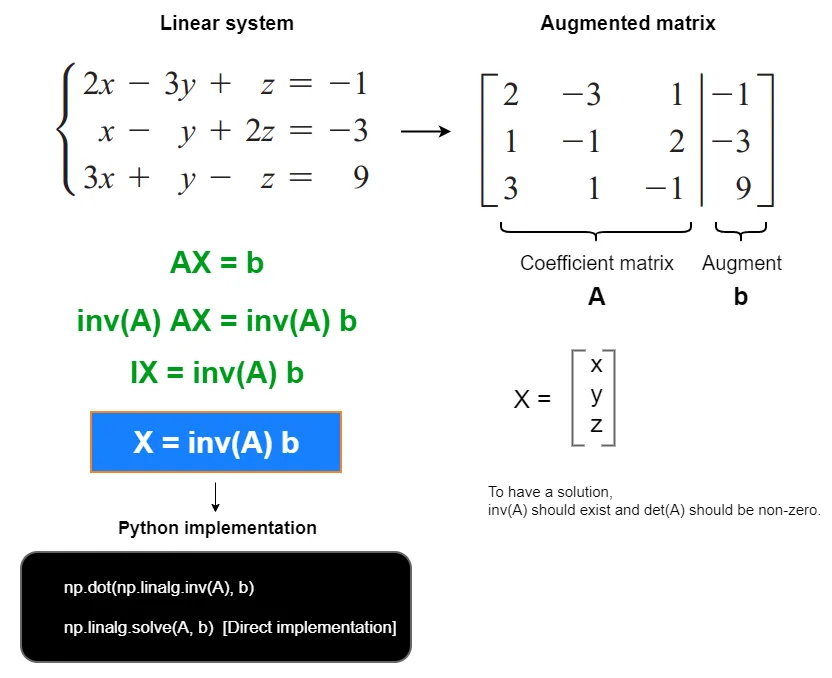
线性代数
A * X = B
s0 = 10
b0 = 10
M0 = np.array((s0,b0))
SK = np.array((20,10))
BD = np.array((11,11))
M = np.array((SK,BD)).T
>>> M
array([[20, 11],
[10, 11]])
K = 14.5
C = np.maximum(SK-K,0)
phi = np.linalg.solve(M,C) #求解线性方程组
>>> phi
array([ 0.55, -0.5 ])
C0 = M0.dot(phi)
>>> C0
0.5
refrence
- 原文作者:winsun
- 原文链接:https://winsun.github.io/fightsec/post/ml_05_numpy/
- 版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可,非商业转载请注明出处(作者,原文链接),商业转载请联系作者获得授权。